Industrial Heat Exchangers
The use of Heat Exchangers, correctly chosen and designed, in industrial processes are of key importance to the industry to ensure energetic efficiency and low environmental footprint. Heat Exchangers transfer energy between two different media. These media can be liquids, gases, biphasic and in some cases even liquids carrying substantial loads of solids. Industrial Heat Exchangers play a central role in the processing industry in applications for heat recovery, heating, cooling, condensation and evaporation, etc.
What are Heat Exchangers?
A Heat Exchanger is an apparatus that transfers heat energy from one media to another. One of the media, at higher temperature (often called Hot Media), will release heat energy and decrease its temperature while the other media, at a colder temperature (often called Cold Media) than the hot media, will receive heat energy and thus increase its temperature.
In some cases, the heat transfer can be in direct contact where the media are intermixed while the energy transfer occurs, for example in direct contact condensers.
Most often it is necessary to keep the media apart to avoid mixing and thus contamination in between them. In these cases, it is necessary to find a correct technical solution that will provide a good thermal transfer and reasonable pressure drop while taking into consideration potential fouling, eventual corrosion by the media or environment, as well as economical aspects such as Initial Investment (CAPEX) and Operational Costs (OPEX). There are several different kinds of heat exchangers on the market and the selection of the correct type is of key importance for overall energy and operational efficiency to minimize environmental footprint and lifetime cost for the process and apparatus. Some of the most common heat exchanger types are: – Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers; – Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers; – Tube in Tube Heat Exchangers; – Welded Plate Heat Exchangers; – Spiral Heat Exchangers; – Lamellar Heat Exchangers, etc.
Industrial Heat Exchangers
Industrial Heat Exchangers are designed to meet the requirements of the process where they will be applied often in a tailor-made solution. Many factors must be taken into consideration for the correct selection depending on the types of media and their physical properties, flow rates, temperatures, pressures, allowable pressure drop, potential fouling, and eventual corrosive media or environment.
- Size and Capacity: Industrial Heat Exchangers will normally be tailor-made for a specific application. Its size and capacity will depend on the design conditions, from very small units with small connections, DN25, and low-pressure ratings and sizes well below 1m and 50kg up to enormous units with large connections, DN650, and very high-pressure ratings and sizes depending of type above 20m and several 10s of tons.
- Materials: Industrial heat exchangers are often made of corrosion-resistant materials, such as various stainless-steel grades, duplex or super duplex steel, SMO, titanium, etc. to withstand harsh process environments and corrosive media. If the Heat Exchanger uses gaskets these also have to be correctly chosen to withstand operating temperatures and have compatibility with the media applied.
- Design: The design of industrial heat exchangers is optimized to meet industrial needs for the specific application, including: – high heat transfer capacity; – pressure and temperature resistance; – reasonable flow velocity and pressure loss; – eventual corrosion and fouling factors; – material definitions; – type of heat exchanger; – ease of maintenance and cleaning, etc..
Types of Industrial Heat Exchangers
Several types of heat exchangers are applicable to industrial processes. The selection of the most suitable one can sometimes be a challenge due to specific process parameters such as flow rates, high temperatures and/or pressures, corrosive or fouling media, footprint requirements, cleaning necessity and downtime for maintenance, spare part needs, durability and life expectancy, etc. Some of the heat exchanger types Erivac can provide are:
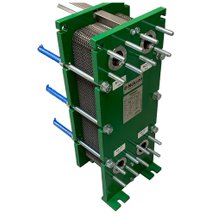
Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers are a type of heat exchanger often used in industrial process applications where temperatures and pressures are relatively low. Corrugated plates are separated by gaskets creating multi-channel passage for the media. The media, separated by the plates, normally flow in countercurrent. Plate pack with gaskets are mounted in frames.
Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers characteristics and advantages:
– Efficient heat transfer: Small channel spacing and corrugated plates ensure good flow velocities and high turbulence for high heat transfer coefficients and efficient heat transfer. Very thin plate thickness ensures very good heat transfer between hot and cold media.
– Compact design: Plate heat exchangers have a compact design, due to high heat transfer coefficients, and take up less space compared to other types of heat exchangers, which can be beneficial in some industrial environments.
– Relatively easy cleaning and maintenance: Plate Heat Exchangers are mounted on frames where the plates and interspacing gaskets are installed. Bolts are securing the plate pack, plates and gaskets, at a specific torque to avoid leakage. These bolts can be loosened to separate the plates for cleaning and changing of gaskets as well as potential substitution of plates to maintain the performance of the heat exchangers over time.
Welded Plate Heat Exchangers
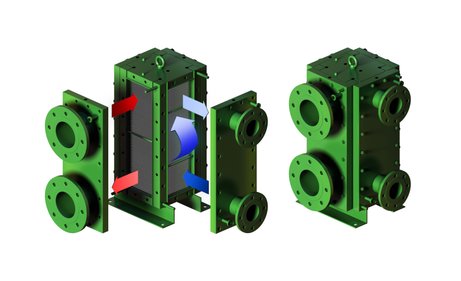
Welded Plate Heat Exchangers are a type of heat exchanger used in industrial process applications, often for semi-fouling or viscous media or when temperature or pressure are higher than technically possible for Gasketed Plate types. Most often corrugated plates are used and these are welded together creating a multi-channel passage for the media. The media, separated by the plates, normally flow in cross flow / counter current (when more than one pass is used). The welded plate pack can be mounted in shells – Plate and Shell Heat Exchangers – or in frames with lids on each side forming a block – Block Heat Exchangers.
Welded Plate Heat Exchangers characteristics and advantages:
– Efficient heat transfer: Relatively small channel spacing (while larger than for conventional gasketed plates) and corrugated plates ensure good flow velocities and high turbulence for high heat transfer coefficients and efficient heat transfer. The relatively thin plate thickness ensures good heat transfer between hot and cold media.
– Compact design: Welded Plate heat exchangers have a compact design, due to high heat transfer coefficients, and take up less space compared to other types of heat exchangers, which can be beneficial in some industrial environments.
– Easy cleaning and maintenance: Welded Plate Heat Exchangers and especially Block Heat Exchangers are easy to clean and need only a minimum of spare parts. Bolts are securing the lids to the frame with the plate pack. These bolts can be loosened to have access to the plate pack from both sides, for each of the two media, for easy cleaning and changing of gaskets for the 04 lids to maintain the performance of the heat exchangers over time.
– Low operational cost: Lower cleaning frequency due to larger channel spacing and lower spare part necessity than for Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers ensure low operational cost.
– Very robust construction: Correct manufacture, thicker plate material, patents for mechanical design together with welding with added material ensures a very robust construction and long lifetime for these Welded Plate Exchangers (Block Type), even for applications with frequent changes in temperature and/or pressure.
– Resistant to contamination: The robust welded design reduces the risk of leakage from one Media side to the other.
Spiral Plate Heat Exchangers
Spiral Plate Heat Exchangers are a type of heat exchanger sometimes used in industrial process applications, for fouling or viscous media, media with considerable solid content, when temperature or pressure are higher than technically possible for Gasketed Plate types or Welded Plate Heat Exchangers.
Spiral heat exchangers has a unique single-channel design using two plate sheets with studs, to create channel spacing, wound around a cylindrical core into a spiral shape. The plates are welded together in such a way that the media are separated from each other and the channels are accessible from one side for each media. The sides of the spiral are bolted shut with heavy circular lids. The flow regime is normally counter flow. Due to the unique, single channel, design these heat exchangers have a self-cleaning effect.
Spiral Plate Heat Exchangers characteristics and advantages:
– Efficient heat transfer: The unique channel configuration in a spiral in combination with good design considering pressure drop and flow velocity ensures high turbulence and thus good heat transfer coefficients and efficient heat transfer.
– Compact design: Spiral Plate heat exchangers have a compact design in comparison to equivalent Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers, due to high heat transfer coefficients, and thus have a smaller footprint.
– Easy cleaning and maintenance: Spiral Plate Heat Exchangers are easy to clean and need only a minimum of spare parts. Bolts are securing the two lids to the spiral body. These bolts can be loosened to have access to the spiral channel from both sides, normally one side for each of the two media, for easy cleaning and changing of gaskets for the 02 lids to maintain the performance of the heat exchangers over time.
– Self-cleaning effect: The unique channel configuration with only one, sometimes two, channels for each media provides a unique self-cleaning effect. When at some point in the channel fouling starts to occur the transversal area at that point will be reduced thus provoking an increase of velocity and turbulence at that point. With the increase of local turbulence dirt/fouling often can be washed out. The self-cleaning effect of the Spiral Plate Heat Exchanger results in longer operation time before they need to be cleaned, either by CIP or opened for mechanical cleaning with hydro jet.
– Low operational cost: Lower cleaning frequency due to larger channel spacing as well as the aforementioned self-cleaning effect and lower spare part necessity than for other types of Heat Exchangers ensure very low operational cost.
– Very robust construction: Correct manufacture, thicker plate material, patents for mechanical design together with excellent welding quality ensures a very robust construction and long lifetime for these Spiral Plate Exchangers, even for applications with frequent changes in temperature and/or pressure.
– Resistant to contamination: The robust welded design reduces the risk of leakage from one Media side to the other.
Tubular heat exchangers with corrugated tubes
Corrugated tube heat exchangers are particularly useful for industrial processes involving heat transfer for slurries and particulate liquids. These heat exchangers consist of two concentric tubes, of which one or both tubes can be corrugated.
Corrugated Tube Heat Exchangers characteristics and advantages:
– Efficient heat transfer: The corrugation of the tubes in combination with good design considering pressure drop and flow velocity ensures high turbulence and thus good heat transfer coefficients and efficient heat transfer.
– Handling of particulate fluids: The corrugated tube design allows the heat exchanger to handle media with considerable viscosity or containing particles, fibers or other particulate materials without the risk of clogging or blockage.
Applicability in specific industries: Corrugated tube heat exchangers are often used in industries that process slurries or particulate fluids, such as the food industry and chemical processes.
Coil Wound Heat Exchangers
Coil wound heat exchangers are one of the most advanced, efficient and energy-saving large-scale heat exchange equipment in the world.
It not only has the advantages of high heat transfer efficiency, compact structure and light weight of plate heat exchangers, but also has the advantages of high pressure and high temperature resistance, good sealing performance, safety and reliability of shell and tube heat exchangers.
Judging from the current situation of global water and energy shortages, this product has broad application in industries with large energy and cooling water consumptions.
– Compact structure and small footprint. Coil wound tube heat exchangers are usually arranged vertically and occupy only about one-tenth of the area of ordinary shell and tube heat exchangers.
– Limited by tube length and transportation, ordinary shell and tube heat exchangers have a maximum heat exchanger area of 3 000 m², while Coil Wound Heat Exchangers have a maximum heat exchanger area of 25 000 m² per shell.
– Up to 8 different media can be heated, condensed or cooled simultaneously.
– The specific design of our Coil Wound Heat Exchangers makes them extremely robust, they can handle much larger temperature and pressure differences than other heat exchanger types.
– Heat exchanger tubes of this high-efficiency heat exchanger adopt a spiral structure, which is equivalent to using countless expansion joints in the heat exchanger. The heat exchanger tubes can expand freely when subjected to temperature changes.
– A very close temperature approach can be achieved, which can effectively recover more heat. The spiral wound heat exchanger tubes are 4 to 6 times longer than the length of the shell side. The temperature approach of ordinary shell and tube heat exchangers is generally about 40°C, while the temperature approach of Coil Wound Heat Exchangers can be within 5°C.
– The tube side media stays in the heat exchange tube bundle for a longer time, and thus condensation can be more complete.
– Due to the spiral design of the tubes, the tube side media must continuously change directions, thus enhancing turbulent flow. This increases heat transfer efficiency and reduces the heat exchange surface area. Compared with ordinary shell and tube heat exchangers, Coil Wound Heat Exchangers’ heat transfer coefficient can be increased up to 6 times.
Conclusion
Industrial heat exchangers play a crucial role in various industries by enabling efficient heat transfer between media. There are several types of Industrial Heat Exchanger and these differ from each other when it comes to size/compactness/footprint, available materials of construction, temperature and pressure resistance, robustness, mechanical design, spare part needs, accessibility and cleanability, operational availability and maintenance frequency, etc. with each type optimized for its industrial needs and process application. With the different types of heat exchangers available, such as gasketed plate heat exchangers, welded plate heat exchangers, shell and tube heat exchangers, spiral heat exchangers and corrugated tube heat exchangers, industries can choose the most suitable one for their specific applications.
By using efficient and reliable heat exchangers, industries can achieve high energy efficiency, cost savings and an optimized production process. Understanding the differences and benefits of different types of heat exchangers is important for choosing the correct or best possible solution to suit the specific needs and requirements of the industry and its process applications as well as taking into consideration initial investment (CAPEX) and operational costs (OPEX) and life expectancy of the heat exchangers etc.